

Call Cognex Sales: 855-4-COGNEX (855-426-4639)
- Contact Us
- Home
- Products
- Machine Vision
- Vision Sensors
Vision sensors are a type of automated solution that solve simple error-proofing applications. Typically, they perform a single function at a time, such as binary classification, defect detection, optical character recognition (OCR), object counting, and assembly verification.
More capable than other types of sensors, including photoelectric, laser, and proximity, vision sensors combine a camera’s ability to take pictures with the processing power of a computer. They analyze acquired images to gather data for inspections or to trigger other devices. Based on criteria set during training, vision sensors look for specific features to identify anomalies on parts or within processes to automate decision-making and quality control activities.

Powered by pre-trained AI, In-Sight SnAPP sensors are designed for ultimate simplicity, providing a fast-and easy-to-deploy solution for novice users with little to no technical experience. They automate a range of error-proofing tasks, including those with variable anomalies.

Leveraging traditional, rule-based vision, In-Sight 2000 vision sensors are intended for intermediate to advanced users that require more robust programming options. They excel at solving applications with consistent or predictable anomalies.

A vision sensor's primary function is to detect an object's presence or absence within a specified region of interest. The output for these types of applications is typically binary, such as “yes/no,” “pass/fail,” or “OK/NG,” and can be used in both product and process-related tasks.
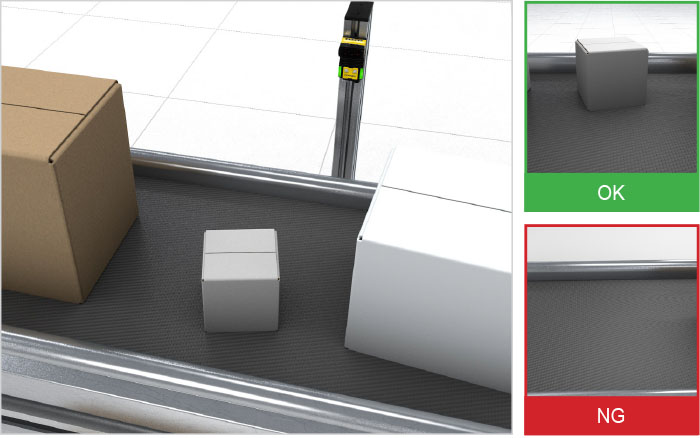
Vision sensors ensure an automated system is running correctly and reduce errors in machine setup. For example, they verify that the system is diverting bad parts, communicating the right information to a centralized database and that parts are coming through the line as intended.

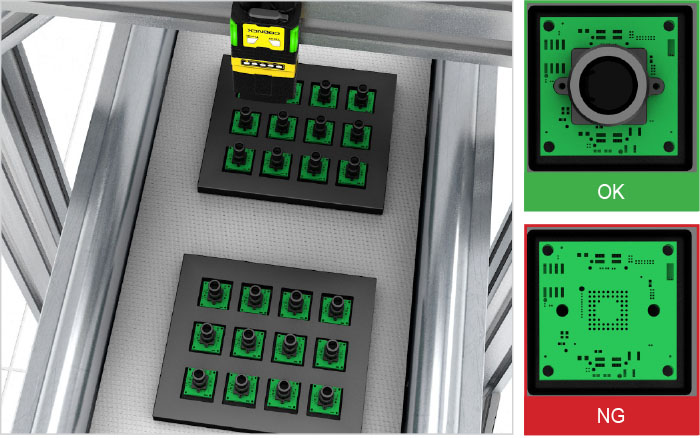
At the most fundamental level, vision sensors perform binary classification. However, they also run multi-class inspections to sort defects into different categories based on multiple features or characteristics and correctly identify parts with variation.
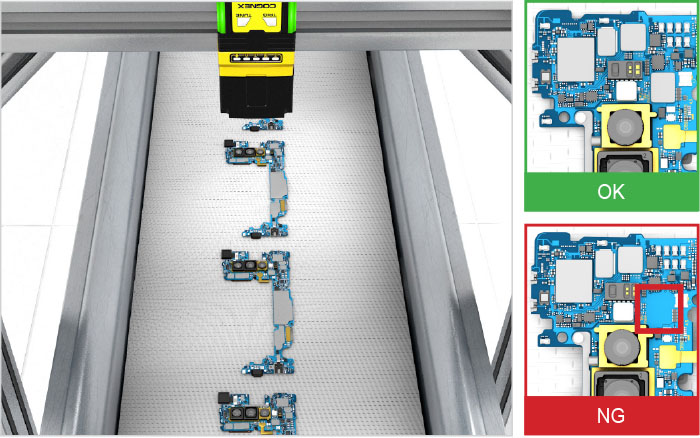
Vision sensors recognize multiple types of components in varying layouts and configurations to automate assembly, or completeness, checks. They locate and confirm whether components are present and correct and identify damaged or missing parts in kitted products.

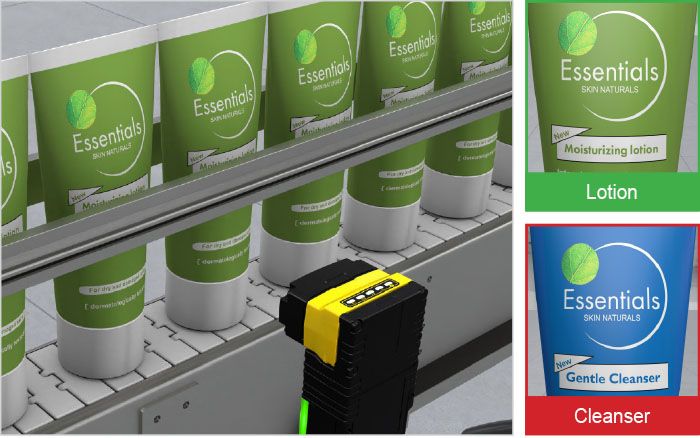
In OCR applications, vision sensors convert alphanumeric text into a machine-readable format for traceability purposes. They can decipher different font types and read characters on reflective, low-contrast, and non-flat surfaces.
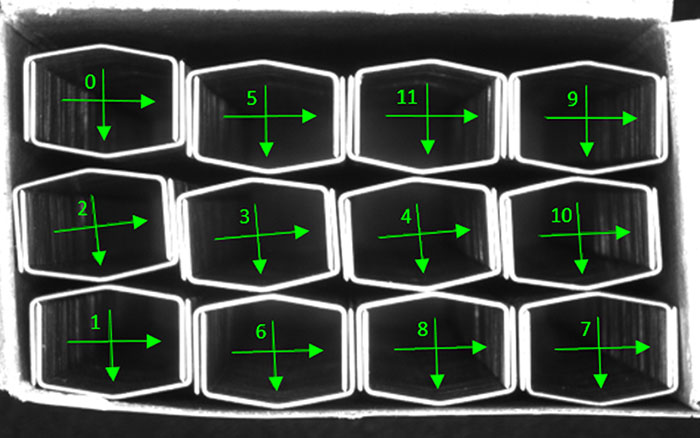
Vision sensors are used in counting applications to verify the correct number of components in a kit or packaged assembly. Similarly, they are also used to ensure parts move down production lines at the correct rate to achieve capacity and throughput targets.
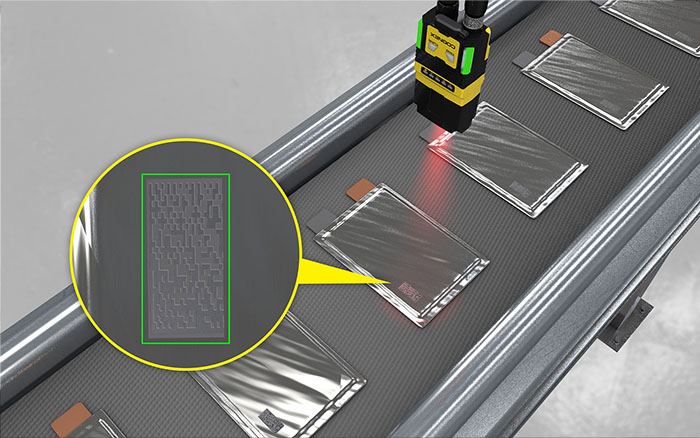
With the ability to read a variety of 1D and 2D barcodes, vision sensors enable manufacturers and logistics facilities to track and trace parts. They interpret codes into usable information, which is then transferred to a centralized system where it can be used to track inventory and shipments, verify product authenticity, and manage returns and recalls.